Choosing the Best Ranch Location
A ranch location refers to the geographic area where a ranch is situated. It encompasses the land, natural surroundings, and environmental conditions that influence its suitability for agricultural, recreational, or conservation purposes. These factors include climate, topography, soil quality, water availability, and accessibility to urban amenities.
Selecting the best ranch location is paramount for the success and sustainability of ranching operations. The location significantly impacts ranch owners and operators’ productivity, profitability, land value, and quality of life. By choosing the right location, ranchers can maximize agricultural yields, optimize resource utilization, mitigate risks, and enhance their investment’s overall viability and long-term value.
Geographic Considerations
Climate and weather patterns play an important role in determining the suitability of a ranch location for agricultural production and outdoor activities. Factors like temperature extremes, precipitation levels, and seasonal variations influence the types of crops that can be grown, the availability of water resources, and the health and well-being of livestock. Selecting a location with a favorable climate and reliable weather patterns can minimize weather-related risks and ensure consistent productivity throughout the year.
Topography and Land Features
Topography and land features encompass the physical characteristics of the terrain, including elevation, slope, soil composition, and natural vegetation. The topography of a ranch location affects drainage patterns, erosion control, and land use options. Flat or gently sloping terrain may suit agricultural cultivation, grazing, or development. In contrast, steep slopes or rugged terrain may be better suited for recreational activities or wildlife habitat conservation. Evaluating topographic features helps identify potential opportunities and constraints for land use and development.
Low Maintenance vs High Maintenance Land
Land is often described as either high maintenance or low maintenance based on the amount of work, cost, and resources needed to keep it functional, attractive, or productive. High maintenance land is typically found in humid or high-rainfall regions where vegetation grows quickly. These areas often include dense brush, invasive species like mesquite or cedar, or improved pastures that require regular mowing, spraying, and fencing. Properties with landscaped elements or irrigated plants add further demands, needing consistent water, pruning, and pest control. In such climates, especially in places like East Texas or the Gulf Coast, landowners must contend with overgrowth, erosion, and even flooding, making routine upkeep more intensive.
In contrast, low maintenance land is usually located in arid or semi-arid climates such as West Texas, where native grasses and sparse desert scrub dominate. These regions naturally suppress excessive plant growth, limiting the need for mowing or spraying. The dry climate also reduces pest and fungal issues, lowering the need for chemical treatment. Flat or gently rolling terrain with drought-tolerant vegetation often requires little more than seasonal inspection or occasional brush clearing. For buyers focused on recreational use, grazing, or long-term conservation, low maintenance land offers a more hands-off, cost-effective option with fewer surprises.
Soil Quality and Fertility
Soil quality and fertility are critical determinants of agricultural productivity and the success of ranching operations. Soil composition, texture, structure, and nutrient content influence the growth and health of crops, forage, and pasture vegetation. Soil testing and analysis help assess soil fertility levels, pH balance, and nutrient deficiencies, guiding land management practices such as fertilization, irrigation, and crop rotation. Choosing a location with fertile soils conducive to agricultural production can enhance yields, reduce input costs, and improve the overall profitability of the ranch.
Water Availability and Quality
Water availability and quality are essential for ranching operations, supporting livestock watering, irrigation, and domestic needs. Factors such as surface water sources (rivers, lakes, ponds), groundwater aquifers, precipitation levels, and water rights influence the reliability and sustainability of water supplies. Assessing water availability and quality helps ensure sufficient water resources for agricultural production, livestock hydration, and ecological conservation. Additionally, monitoring water quality parameters such as pH, turbidity, and contaminants safeguards human and animal health and compliance with environmental regulations.
Accessibility And Infrastructure
Proximity to Urban Centers and Amenities
The proximity of a ranch location to urban centers and amenities affects convenience, accessibility, and market opportunities for ranch owners and operators. Proximity to cities or towns provides access to essential services, markets, healthcare facilities, educational institutions, and recreational amenities. It facilitates transportation logistics, supply chain management, and business operations, reducing travel time and costs for ranch activities. Moreover, proximity to urban areas may enhance property values and attract potential buyers or renters seeking rural lifestyle properties within commuting distance of metropolitan amenities.
Transportation Infrastructure
Transportation infrastructure, including roads, highways, railroads, airports, and ports, influences the connectivity and accessibility of a ranch location to regional and national markets. Well-developed transportation networks facilitate the movement of goods, equipment, and personnel to and from the ranch, supporting agricultural marketing, distribution, and logistics.
Access to major transportation corridors improves market access, lessens transportation costs, and enhances the competitiveness of ranch products in domestic and international markets. Evaluating transportation infrastructure helps identify corridors, shipping routes, and logistical hubs that optimize connectivity and market reach for ranching operations.
Availability Of Utilities (Water, Electricity, Internet)
Access to important utilities such as water, electricity, and internet connectivity is vital for ranching operations and residential living on the property. Reliable water supplies support domestic use, irrigation, and livestock watering needs, ensuring the health and productivity of ranch operations. Electricity infrastructure enables power supply for residential, agricultural, and industrial purposes, including lighting, heating, cooling, and equipment operation. High-speed internet access facilitates communication, data management, online marketing, and remote monitoring of ranch activities. Assessing the availability and reliability of utilities helps ensure operational efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life for ranch occupants.
Existing Infrastructure On The Property (Roads, Buildings)
Existing infrastructure on the property, such as roads, bridges, fences, buildings, and utilities, influences the ranch’s development potential and operational efficiency. Well-maintained roads provide access to different areas of the property for transportation, livestock handling, and recreational activities. Functional buildings and facilities, such as barns, corrals, storage sheds, and housing structures, support agricultural operations, equipment storage, and residential accommodation for ranch personnel. Assessing the condition and adequacy of existing infrastructure helps identify maintenance needs, improvement opportunities, and development constraints for the ranch property.
Choosing the best ranch location involves carefully considering geographic factors, accessibility, infrastructure, and environmental suitability. By evaluating these fundamental considerations, ranch owners and operators can identify optimal locations that maximize productivity, profitability, and quality of life for sustainable ranching operations.
Legal And Regulatory Factors
Zoning Regulations For Ranching Activities
Zoning regulations will dictate how land can be used within specific geographic areas and play a critical role in determining the permissibility of ranching activities. These regulations may designate areas for agricultural use, conservation, or residential development, with varying restrictions and requirements for ranch operations. Understanding zoning regulations helps ensure compliance with land use restrictions, setback requirements, building codes, and environmental standards when establishing or expanding ranching operations.
Environmental Regulations and Land Use Restrictions
Environmental regulations govern land use practices, resource management, and conservation efforts to protect natural ecosystems, water quality, and wildlife habitats. These regulations include restrictions on water usage, soil erosion control measures, habitat preservation, and endangered species protection. Compliance with environmental regulations helps mitigate ecological impacts, minimize legal liabilities, and maintain ecosystem integrity for sustainable ranching practices.
Permitting Requirements for Development And Operations
Permitting requirements govern the approval process for land development, construction, and operational activities on ranch properties. Depending on the scope and proposed activities, permits may be required for land clearing, building construction, water rights allocation, wastewater discharge, and wildlife management. Navigating the permitting process involves obtaining approvals from local, state, and federal agencies, conducting environmental assessments, and addressing community concerns. Compliance with permitting requirements ensures legal authorization and regulatory compliance for ranch development and operations.
Market Demand and Trends
Demographics of Potential Buyers Or Renters
Understanding the demographics of potential buyers or renters is essential for assessing market demand and tailoring ranch properties to meet consumer preferences. Demographic factors like age, income level, occupation, lifestyle preferences, and recreational interests influence the demand for rural properties. Analyzing demographic trends helps identify target markets, develop marketing strategies, and customize property offerings to appeal to specific buyer segments.
Market Trends In Ranching And Rural Real Estate
Market trends in ranching and rural real estate provide insights into prevailing market conditions, pricing dynamics, and investment opportunities. Economic trends, interest rates, commodity prices, and population growth impact market demand and property values. Monitoring market trends helps investors identify emerging opportunities, assess competitive landscapes, and adapt investment strategies to changing market conditions.
Consumer Preferences for Ranch Properties
Consumer preferences for ranch properties vary based on lifestyle preferences, recreational interests, and desired amenities. Some buyers may prioritize agricultural production, livestock facilities, or hunting and fishing opportunities, while others may seek recreational amenities, scenic views, or conservation values. Understanding consumer preferences helps attract potential buyers and maximize property value by tailoring property offerings, marketing messages, and sales strategies.
Natural Resources and Potential Uses
Evaluation Of Natural Resources (Water, Timber, Minerals)
Assessing natural resources such as water, timber, and minerals is crucial for understanding ranch properties’ productive capacity and potential uses. Water resources support agricultural irrigation, livestock hydration, and recreational activities, while timber resources provide forestry management and harvesting opportunities. Additionally, mineral rights may offer revenue potential through extraction activities such as mining or oil and gas production. Evaluating natural resources helps identify opportunities for resource utilization, conservation, and sustainable land management practices.
Suitability For Agricultural, Livestock, Or Recreational Activities
The suitability of ranch properties for agricultural, livestock, or recreational activities depends on factors such as soil quality, climate conditions, topography, and land features. Assessing land suitability involves evaluating soil fertility, drainage, pasture quality, and wildlife habitat. Properties with fertile soils, abundant water resources, and diverse ecosystems may be well-suited for agricultural production, grazing, or outdoor recreation. Understanding land suitability helps optimize land use planning, resource allocation, and operational management for sustainable ranching practices.
Potential for Conservation Or Eco-Tourism Ventures
Ranch properties may offer opportunities for conservation or eco-tourism ventures aimed at preserving natural habitats, biodiversity, and cultural heritage. Conservation initiatives such as wildlife habitat restoration, wetland conservation, or riparian buffer zones contribute to ecosystem health and biodiversity conservation. Additionally, eco-tourism activities such as birdwatching, hiking, or nature photography capitalize on ranch landscapes’ scenic beauty and ecological richness. Exploring conservation and eco-tourism opportunities enhances ranch properties’ ecological value, recreational appeal, and economic sustainability.
Risk Assessment
Evaluation of Environmental Risks (Floods, Wildfires)
Assessing environmental risks such as floods, wildfires, and natural disasters is essential for understanding potential hazards and implementing risk mitigation strategies. Factors such as proximity to floodplains, wildfire-prone areas, or seismic fault lines influence property vulnerability to natural hazards. Implementing floodplain management, fire mitigation, and emergency preparedness measures helps reduce property risks and safeguard human and ecological resources.
Economic Risks (Market Volatility, Financial Stability)
Evaluating economic risks such as market volatility, financial instability, and economic downturns helps assess investment viability and financial resilience. Factors such as fluctuations in commodity prices, interest rates, and currency exchange rates impact ranching profitability and investment returns. Implementing risk management strategies like diversification, hedging, and financial planning helps mitigate economic risks and ensure long-term financial sustainability.
Social and Political Risks (Community Relations, Regulatory Changes)
Assessing social and political risks such as community relations, regulatory changes, and geopolitical instability is crucial for managing reputational risks and regulatory compliance. Community opposition, land use conflicts, or regulatory uncertainties may impact property values and operational continuity. Engaging stakeholders, building positive relationships, and staying informed about regulatory developments help mitigate social and political risks and foster a supportive operating environment.
Cost Considerations
Purchase Price of the Property
The property’s purchase price is a significant cost consideration in ranch investing, impacting overall investment affordability and financial feasibility. Location, size, amenities, natural resources, and market demand influence property valuations and pricing dynamics. Thorough market research, property appraisals, and comparative market analyses help assess property values and negotiate favorable purchase terms.
Development and Improvement Costs
Development and improvement costs encompass expenses related to land development, infrastructure construction, and property enhancements to optimize land use and operational efficiency. These costs may include site preparation, road construction, utility installation, building construction, fencing, and landscaping. Budgeting for development and improvement costs involves estimating project scope, obtaining construction bids, and effectively managing project timelines and budgets.
Operational Expenses (Taxes, Utilities, Maintenance)
Operational expenses include ongoing property ownership, maintenance, and management costs. These expenses may include property taxes, insurance premiums, utility bills (water, electricity, internet), maintenance and repair costs, equipment depreciation, and labor expenses. Estimating operational expenses helps forecast cash flow, budget for recurring fees, and evaluate investment returns over the property’s lifecycle.
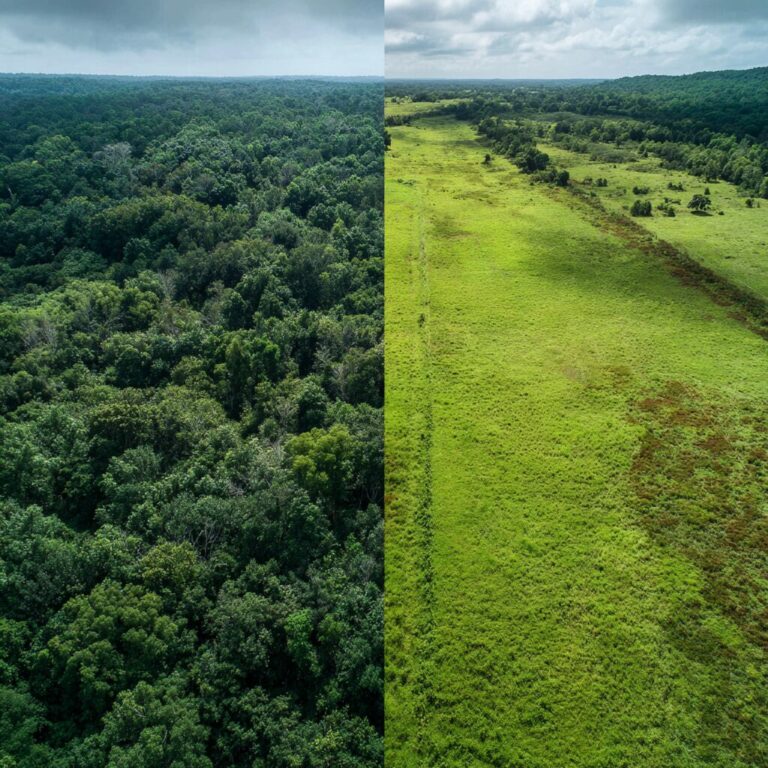

Long-Term Vision And Goals
Alignment with Personal Or Business Objectives
Aligning ranch investments with personal or business objectives ensures strategic alignment and goal attainment over the long term. Lifestyle preferences, financial goals, risk tolerance, and legacy planning influence investment decision-making and asset allocation strategies. A clear vision and mission statement helps define investment priorities, values, and objectives to guide decision-making and performance evaluation.
Sustainability and Stewardship Values
Embracing sustainability and stewardship values promotes responsible land management, environmental conservation, and community engagement in ranching operations. Sustainable practices like soil conservation, water management, habitat restoration, and wildlife conservation enhance ecological resilience, biodiversity, and ecosystem services. Integrating sustainability principles into ranch management practices fosters long-term environmental, social, and economic benefits for future generations.
Potential for Future Growth And Appreciation
Assessing future growth and appreciation potential involves evaluating market dynamics, investment trends, and property value appreciation prospects over time: population growth, urbanization trends, infrastructure development, and economic growth impact property demand and appreciation potential. Investing in properties with growth potential, strategic location, and value-added opportunities helps maximize investment returns and capitalize on emerging market trends.
Conclusion
Choosing the best ranch location involves evaluating various factors, including legal and regulatory considerations, market demand and trends, natural resources, risk assessment, cost considerations, and long-term vision and goals. By carefully assessing these fundamental considerations, ranch owners and investors can identify optimal locations that maximize productivity, profitability, sustainability, and long-term value.
Selecting an ideal ranch location requires thorough due diligence, strategic planning, and informed decision-making to ensure alignment with personal or business objectives. Key considerations include geographic factors, accessibility and infrastructure, legal and regulatory factors, market demand and trends, natural resources and potential uses, risk assessment, cost considerations, and long-term vision and goals. By integrating these considerations into the site selection process, ranch owners and investors can make informed decisions that optimize investment returns and achieve sustainable ranching success.



